How does the IT industry manage project accounting
July 19 2023Victor Terry is the owner of a software business with around 200 people. The company attaches great importance to large customers . To Victor's headache, he wanted to know how much each client cost and what benefit it brought. CloudCC Profit Cloud provides the enterprise with a customer-oriented accounting management solution.
● Estimated budget
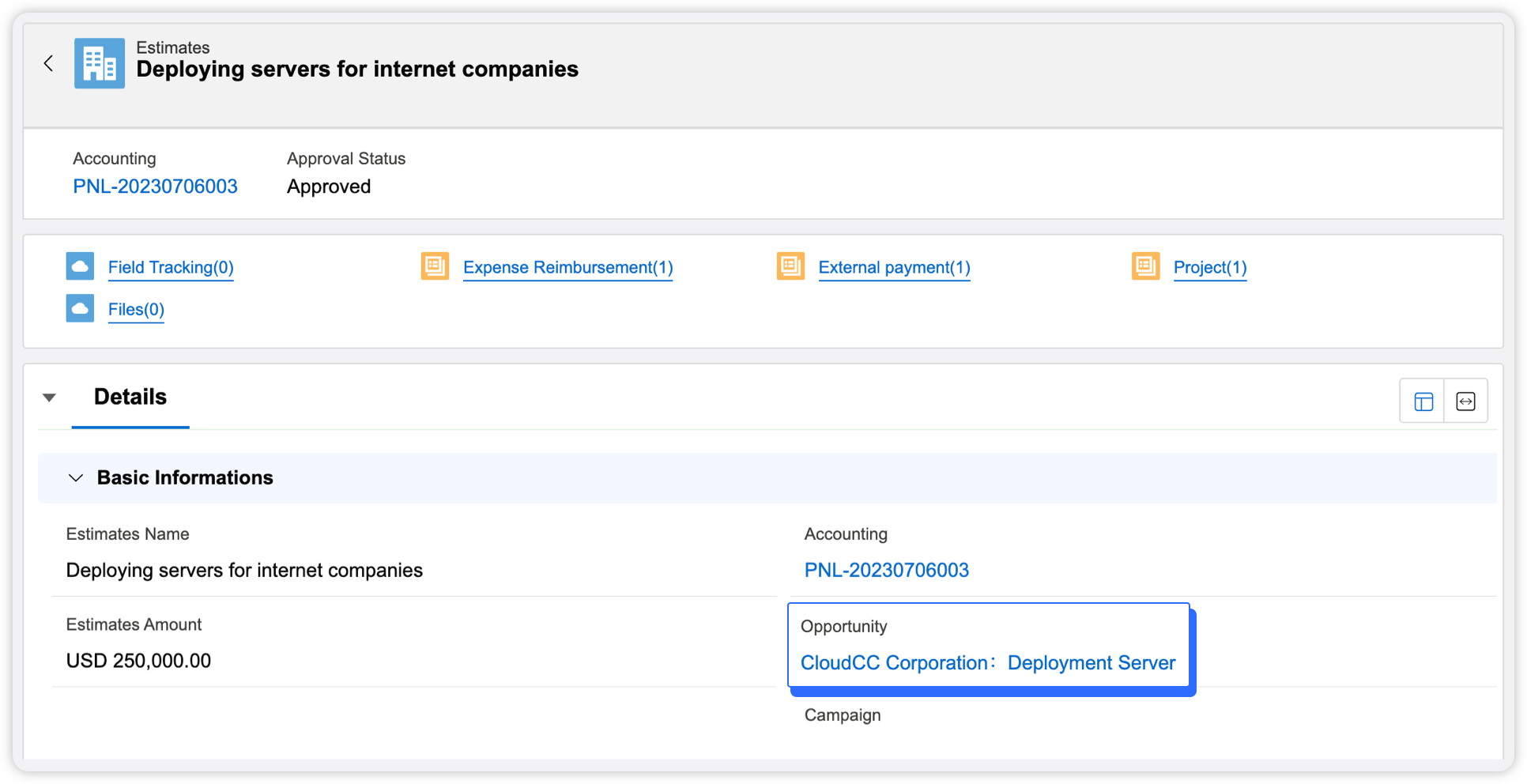
Rose Hart and her sales team members are following up a customer. She created a business opportunity in the CloudCC system with an estimated signing amount of $500,000 . She creates "Estimates" under business opportunities, estimating sales expenses of $2,000 and product costs of $50,000 ( according to company regulations, 10% of the contracted amount is allocated as product cost ).
Next, evaluate the pre-sales expenses and pre-sales man-hours in the budget estimate. She shared the estimated budget with Alex Wang, the pre-sales manager. Alex will dispatch 3 pre-sales personnel according to customer needs, and the required working hours are 48Hrs. According to the average working hour rate of the company's pre-sales engineers, the system calculates the Labor rate, calculate labor cost before sale as $2400 . At the same time, the travel and other expenses required for pre-sales work are $600.
Once the project is signed, it still needs to be delivered, so the delivery cost and delivery time need to be evaluated. Rose shared the estimate with the delivery manager Jack Chen, and the estimated delivery man-hour was 720Hrs, and the delivery man-hour cost was $43,200 . The delivery fee is $3000 .
After filling in the above basic elements of the budget estimate, the system will automatically calculate the gross profit and gross profit rate. The calculation formula is as follows: Estimated gross profit = estimated contract amount of business opportunity $500,000-sales cost $2,000-product cost $50,000-pre-sales cost $600-pre-sales man-hour cost $2,400-delivery cost $3,000-delivery man-hour cost $43,200=$398,800
Estimated gross profit margin = gross profit / business opportunity estimated contract amount = 79.76%
After the budget proposal submitted by Rose is approved, the budget proposal will come into force.
● Final accounts during the budgetary period
In the process of following up on the opportunity, the sale incurred an actual cost of $1,700 and a pre-sales cost of $550. They use the CloudCC expense module for reimbursement. After the reimbursement is approved, these expenses will be aggregated to the final settlement module of the budget estimate, and will be aggregated to the profit and loss.
In terms of pre-sales working hours, Alex created a pre-sales project to manage the pre-sales work, created tasks under the project and assigned them to pre-sales personnel Anna Mathis and Trevor Lambert respectively, and the planned working hours were 32Hrs . The pre-sales personnel start to record the actual work content according to the assigned tasks, and the actual total working hours are 24Hrs . Anna Mathis and Trevor Lambert's cost labor rate is $50, Alex's cost labor rate is $70, and the actual pre-sales cost is $1,360 .
The total expenses submitted by sales, pre-sales, and delivery personnel cannot exceed the estimated expenses, and the actual working hours recorded cannot exceed the planned working hours, and the planned working hours cannot exceed the estimated working hours.
As a result, costs are strictly controlled.
Estimated selling expenses: $2,000, actual selling expenses: $1,700
Estimated pre-sales cost: $600, actual pre-sales cost: $550
Estimated pre-sale man-hour cost: $2,400, actual pre-sale man-hour cost: $1,360
● Budget
After the cooperation of the sales and pre-sales teams, the contract was finally signed with the customer, and the contract amount was $450,000 . Create a budget under the contract. In the budget, the sales cost is $500, the delivery cost is $6,500, the delivery man-hour is 1,440Hrs, the delivery man-hour cost is $86,400, the business cost is $10,000, and the product cost is $45,000.
Budget gross profit = contract signing amount $450,000-sales cost $500 - delivery cost $6,500-delivery man-hour cost $86,400-office cost $10,000-product cost $45,000=$301,600 Budget gross profit margin = budget gross profit / contract signing amount = 67.02%
● Final Accounts for Budget Period
After the budget becomes effective, sales will be reimbursed $240 and deliveries will be reimbursed $6,350. Jack creates deliverables in the system and splits tasks to dispatch to project members Claire Lyman and Karen Glover. The total working hours of dispatch tasks is 1,440Hrs . Jack, Claire, and Karen work according to the dispatched tasks, and use TimeSheet to record the daily work, and record the working hours as 400Hrs, 300Hrs, and 300Hrs respectively. The system calculates the delivery man-hour cost of each person based on the cost man-hour rate of each person, totaling $61,000
Jack Chen's cost and hourly rate is $70, and the labor cost is $70*400Hrs=$28,000
Claire Lyman's cost and hourly rate is $60, and the labor cost is $60*300Hrs=$18,000
Karen Glover's cost and hourly rate is $50, and the labor cost is $50*300Hrs=$15,000
Estimated Selling Fee: $500, Actual Selling Fee: $240
Estimated Delivery Cost: $6,500, Actual Delivery Cost: $6,350
Estimated delivery man-hour cost: $86,400, actual delivery man-hour cost: $61,000
● profit and loss
Profit and loss summarizes estimates, budgets, and final accounts. The more critical part of profit and loss is the calculation of various types of final settlement gross profit. These final accounts gross profits can be used at different times, and the analysis is as follows:
● E-category gross profit
Gross profit calculated using the opportunity amount as revenue minus actual costs incurred is called Class B gross profit. The system calculates the actual cost according to the cost of sales, pre-sales, delivery and submission, external payment, and actual man-hours under the project.
Gross profit of category E settlement = business opportunity amount $500,000-sales expenses $1,940 -product cost $45,000- business cost $10,000-pre-sales expense $550 - pre-sales man-hour cost $1,360-delivery cost $6,350-delivery man-hour cost $61,000=373,800 E-category final settlement gross profit margin = E-category final settlement gross profit / business opportunity amount = 74.76%
● Class B Gross Profit
Gross profit calculated using the contract amount as revenue minus actual costs incurred is called Class B gross profit. The system calculates the actual cost according to the cost of sales, pre-sales, delivery and submission, external payment, and actual man-hours under the project.
Gross profit of Class B settlement = contract amount $450,000-sales expenses $1,940 -product cost $45,000-business cost $10,000- pre-sales expense $550 - pre-sales man-hour cost $1,360-delivery cost $6,350-delivery man-hour cost $61,000=323,800 Gross profit margin of category B final accounts = gross profit of category B final accounts / contract signing amount = 71.95%
● P-category final accounts gross profit
The gross profit calculated on the basis of the actual cash collection income on the cash collection record under the contract minus the actual incurred costs is called the P category final settlement gross profit.
Gross profit of final settlement of category P =receipt amount $300,000-sales cost $1,940 -product cost $45,000-business cost $10,000- pre-sales cost $550 - pre-sales man-hour cost $1,360-delivery cost $6,350-delivery man-hour cost $61,000=173,800
P category final settlement gross profit rate = P category final settlement gross profit / repayment amount = 57.93%
● T-category final settlement gross profit
Gross profit calculated based on the sum of Class B and Class E revenue as revenue minus actual costs incurred is called Class T final settlement gross profit.
T-category final settlement gross profit = contract amount $450,000+business opportunity amount $500,000-sales cost $1,940 -product cost $45,000-business cost $10,000-pre- sales cost $550-pre-sale man-hour cost $1,360 - delivery cost $6,350-delivery man-hour cost $61,000=798,000
T-category final settlement gross profit margin = T-category final settlement gross profit/contract amount $450,000+business opportunity amount $500,000=84%
● Effect
Victor Terry said: By using CloudCC Profit Cloud, I can clearly understand the investment cost and gross profit at the stage of business opportunity project approval. Not only that, if the salesman still fails to win the order after spending the estimated cost, I can consider stopping the loss in time to prevent more cost investment and no money. And I can clearly see the final money earned through the actual expenses and costs recorded line by line.